java.lang
Class String
java.lang.Object
|
+--java.lang.String
- public final class String
- extends Object
- implements Serializable, Comparable
The String class represents character strings. All
string literals in Java programs, such as "abc", are
implemented as instances of this class.
Strings are constant; their values cannot be changed after they
are created. String buffers support mutable strings.
Because String objects are immutable they can be shared. For example:
String str = "abc";
is equivalent to:
char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String str = new String(data);
Here are some more examples of how strings can be used:
System.out.println("abc");
String cde = "cde";
System.out.println("abc" + cde);
String c = "abc".substring(2,3);
String d = cde.substring(1, 2);
The class String includes methods for examining
individual characters of the sequence, for comparing strings, for
searching strings, for extracting substrings, and for creating a
copy of a string with all characters translated to uppercase or to
lowercase.
The Java language provides special support for the string
concatentation operator ( + ), and for conversion of
other objects to strings. String concatenation is implemented
through the StringBuffer class and its
append method.
String conversions are implemented through the method
toString, defined by Object and
inherited by all classes in Java. For additional information on
string concatenation and conversion, see Gosling, Joy, and Steele,
The Java Language Specification.
- Since:
- JDK1.0
- See Also:
Object.toString(),
StringBuffer,
StringBuffer.append(boolean),
StringBuffer.append(char),
StringBuffer.append(char[]),
StringBuffer.append(char[], int, int),
StringBuffer.append(double),
StringBuffer.append(float),
StringBuffer.append(int),
StringBuffer.append(long),
StringBuffer.append(java.lang.Object),
StringBuffer.append(java.lang.String), Serialized Form
|
Constructor Summary |
String()
Initializes a newly created String object so that it
represents an empty character sequence. |
String(byte[] bytes)
Construct a new String by converting the specified array
of bytes using the platform's default character encoding. |
String(byte[] ascii,
int hibyte)
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.
As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
String constructors that take a character-encoding name or
that use the platform's default encoding. |
String(byte[] bytes,
int offset,
int length)
Construct a new String by converting the specified
subarray of bytes using the platform's default character encoding. |
String(byte[] ascii,
int hibyte,
int offset,
int count)
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.
As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
String constructors that take a character-encoding name or
that use the platform's default encoding. |
String(byte[] bytes,
int offset,
int length,
String enc)
Construct a new String by converting the specified
subarray of bytes using the specified character encoding. |
String(byte[] bytes,
String enc)
Construct a new String by converting the specified array
of bytes using the specified character encoding. |
String(char[] value)
Allocates a new String so that it represents the
sequence of characters currently contained in the character array
argument. |
String(char[] value,
int offset,
int count)
Allocates a new String that contains characters from
a subarray of the character array argument. |
String(String value)
Initializes a newly created String object so that it
represents the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other
words, the newly created string is a copy of the argument string. |
String(StringBuffer buffer)
Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters
currently contained in the string buffer argument. |
|
Method Summary |
char |
charAt(int index)
Returns the character at the specified index. |
int |
compareTo(Object o)
Compares this String to another Object. |
int |
compareTo(String anotherString)
Compares two strings lexicographically. |
int |
compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case considerations. |
String |
concat(String str)
Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string. |
static String |
copyValueOf(char[] data)
Returns a String that is equivalent to the specified character array. |
static String |
copyValueOf(char[] data,
int offset,
int count)
Returns a String that is equivalent to the specified character array. |
boolean |
endsWith(String suffix)
Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix. |
boolean |
equals(Object anObject)
Compares this string to the specified object. |
boolean |
equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
Compares this String to another String,
ignoring case considerations. |
byte[] |
getBytes()
Convert this String into bytes according to the platform's
default character encoding, storing the result into a new byte array. |
void |
getBytes(int srcBegin,
int srcEnd,
byte[] dst,
int dstBegin)
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert characters into bytes.
As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
getBytes(String enc) method, which takes a
character-encoding name, or the getBytes() method, which
uses the platform's default encoding. |
byte[] |
getBytes(String enc)
Convert this String into bytes according to the specified
character encoding, storing the result into a new byte array. |
void |
getChars(int srcBegin,
int srcEnd,
char[] dst,
int dstBegin)
Copies characters from this string into the destination character
array. |
int |
hashCode()
Returns a hashcode for this string. |
int |
indexOf(int ch)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified character. |
int |
indexOf(int ch,
int fromIndex)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified character, starting the search at the specified index. |
int |
indexOf(String str)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified substring. |
int |
indexOf(String str,
int fromIndex)
Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified substring, starting at the specified index. |
String |
intern()
Returns a canonical representation for the string object. |
int |
lastIndexOf(int ch)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
specified character. |
int |
lastIndexOf(int ch,
int fromIndex)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
specified character, searching backward starting at the specified
index. |
int |
lastIndexOf(String str)
Returns the index within this string of the rightmost occurrence
of the specified substring. |
int |
lastIndexOf(String str,
int fromIndex)
Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of
the specified substring. |
int |
length()
Returns the length of this string. |
boolean |
regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase,
int toffset,
String other,
int ooffset,
int len)
Tests if two string regions are equal. |
boolean |
regionMatches(int toffset,
String other,
int ooffset,
int len)
Tests if two string regions are equal. |
String |
replace(char oldChar,
char newChar)
Returns a new string resulting from replacing all occurrences of
oldChar in this string with newChar. |
boolean |
startsWith(String prefix)
Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix. |
boolean |
startsWith(String prefix,
int toffset)
Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix beginning
a specified index. |
String |
substring(int beginIndex)
Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. |
String |
substring(int beginIndex,
int endIndex)
Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. |
char[] |
toCharArray()
Converts this string to a new character array. |
String |
toLowerCase()
Converts all of the characters in this String to lower
case using the rules of the default locale, which is returned
by Locale.getDefault. |
String |
toLowerCase(Locale locale)
Converts all of the characters in this String to lower
case using the rules of the given Locale. |
String |
toString()
This object (which is already a string!) is itself returned. |
String |
toUpperCase()
Converts all of the characters in this String to upper
case using the rules of the default locale, which is returned
by Locale.getDefault. |
String |
toUpperCase(Locale locale)
Converts all of the characters in this String to upper
case using the rules of the given locale. |
String |
trim()
Removes white space from both ends of this string. |
static String |
valueOf(boolean b)
Returns the string representation of the boolean argument. |
static String |
valueOf(char c)
Returns the string representation of the char
argument. |
static String |
valueOf(char[] data)
Returns the string representation of the char array
argument. |
static String |
valueOf(char[] data,
int offset,
int count)
Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of the
char array argument. |
static String |
valueOf(double d)
Returns the string representation of the double argument. |
static String |
valueOf(float f)
Returns the string representation of the float argument. |
static String |
valueOf(int i)
Returns the string representation of the int argument. |
static String |
valueOf(long l)
Returns the string representation of the long argument. |
static String |
valueOf(Object obj)
Returns the string representation of the Object argument. |
CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
public static final Comparator CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER
- Returns a Comparator that orders
String objects as by
compareToIgnoreCase.
Note that this Comparator does not take locale into account,
and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
The java.text package provides Collators to allow
locale-sensitive ordering.
- See Also:
Collator.compare(String, String)- Since:
- JDK1.2
String
public String()
- Initializes a newly created
String object so that it
represents an empty character sequence.
String
public String(String value)
- Initializes a newly created
String object so that it
represents the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other
words, the newly created string is a copy of the argument string.
- Parameters:
value - a String.
String
public String(char[] value)
- Allocates a new
String so that it represents the
sequence of characters currently contained in the character array
argument. The contents of the character array are copied; subsequent
modification of the character array does not affect the newly created
string.
- Parameters:
value - the initial value of the string.- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
value is null.
String
public String(char[] value,
int offset,
int count)
- Allocates a new
String that contains characters from
a subarray of the character array argument. The offset
argument is the index of the first character of the subarray and
the count argument specifies the length of the
subarray. The contents of the subarray are copied; subsequent
modification of the character array does not affect the newly
created string.
- Parameters:
value - array that is the source of characters.offset - the initial offset.count - the length.- Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if the
offset
and count arguments index characters outside
the bounds of the value array.- NullPointerException - if
value is
null.
String
public String(byte[] ascii,
int hibyte,
int offset,
int count)
- Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.
As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
String constructors that take a character-encoding name or
that use the platform's default encoding.- Allocates a new
String constructed from a subarray
of an array of 8-bit integer values.
The offset argument is the index of the first byte
of the subarray, and the count argument specifies the
length of the subarray.
Each byte in the subarray is converted to a
char as specified in the method above.
- Parameters:
ascii - the bytes to be converted to characters.hibyte - the top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode character.offset - the initial offset.count - the length.- Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if the
offset
or count argument is invalid.- NullPointerException - if
ascii is
null. - See Also:
String(byte[], int),
String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String),
String(byte[], int, int),
String(byte[], java.lang.String),
String(byte[])
String
public String(byte[] ascii,
int hibyte)
- Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.
As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
String constructors that take a character-encoding name or
that use the platform's default encoding.- Allocates a new
String containing characters
constructed from an array of 8-bit integer values. Each character
cin the resulting string is constructed from the
corresponding component b in the byte array such that:
c == (char)(((hibyte & 0xff) << 8)
| (b & 0xff))
- Parameters:
ascii - the bytes to be converted to characters.hibyte - the top 8 bits of each 16-bit Unicode character.- Throws:
- NullPointerException - If
ascii is
null. - See Also:
String(byte[], int, int, java.lang.String),
String(byte[], int, int),
String(byte[], java.lang.String),
String(byte[])
String
public String(byte[] bytes,
int offset,
int length,
String enc)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- Construct a new
String by converting the specified
subarray of bytes using the specified character encoding. The length of
the new String is a function of the encoding, and hence may
not be equal to the length of the subarray.
- Parameters:
bytes - The bytes to be converted into charactersoffset - Index of the first byte to convertlength - Number of bytes to convertenc - The name of a character encoding- Throws:
- UnsupportedEncodingException - If the named encoding is not supported
IndexOutOfBoundsException if the
offset
and count arguments index characters outside
the bounds of the value array. - Since:
- JDK1.1
String
public String(byte[] bytes,
String enc)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- Construct a new
String by converting the specified array
of bytes using the specified character encoding. The length of the new
String is a function of the encoding, and hence may not be
equal to the length of the byte array.
- Parameters:
bytes - The bytes to be converted into charactersenc - A character-encoding name- Throws:
- UnsupportedEncodingException - If the named encoding is not supported
- Since:
- JDK1.1
String
public String(byte[] bytes,
int offset,
int length)
- Construct a new
String by converting the specified
subarray of bytes using the platform's default character encoding. The
length of the new String is a function of the encoding, and
hence may not be equal to the length of the subarray.
- Parameters:
bytes - The bytes to be converted into charactersoffset - Index of the first byte to convertlength - Number of bytes to convert- Since:
- JDK1.1
String
public String(byte[] bytes)
- Construct a new
String by converting the specified array
of bytes using the platform's default character encoding. The length of
the new String is a function of the encoding, and hence may
not be equal to the length of the byte array.
- Parameters:
bytes - The bytes to be converted into characters- Since:
- JDK1.1
String
public String(StringBuffer buffer)
- Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters
currently contained in the string buffer argument. The contents of
the string buffer are copied; subsequent modification of the string
buffer does not affect the newly created string.
- Parameters:
buffer - a StringBuffer.- Throws:
- NullPointerException - If
buffer is
null.
length
public int length()
- Returns the length of this string.
The length is equal to the number of 16-bit
Unicode characters in the string.
- Returns:
- the length of the sequence of characters represented by this
object.
charAt
public char charAt(int index)
- Returns the character at the specified index. An index ranges
from
0 to length() - 1. The first character
of the sequence is at index 0, the next at index
1, and so on, as for array indexing.
- Parameters:
index - the index of the character.- Returns:
- the character at the specified index of this string.
The first character is at index
0. - Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if the
index
argument is negative or not less than the length of this
string.
getChars
public void getChars(int srcBegin,
int srcEnd,
char[] dst,
int dstBegin)
- Copies characters from this string into the destination character
array.
The first character to be copied is at index srcBegin;
the last character to be copied is at index srcEnd-1
(thus the total number of characters to be copied is
srcEnd-srcBegin). The characters are copied into the
subarray of dst starting at index dstBegin
and ending at index:
dstbegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
- Parameters:
srcBegin - index of the first character in the string
to copy.srcEnd - index after the last character in the string
to copy.dst - the destination array.dstBegin - the start offset in the destination array.- Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - If any of the following
is true:
srcBegin is negative.
srcBegin is greater than srcEnd
srcEnd is greater than the length of this
string
dstBegin is negative
dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin) is larger than
dst.length
- NullPointerException - if
dst is null
getBytes
public void getBytes(int srcBegin,
int srcEnd,
byte[] dst,
int dstBegin)
- Deprecated. This method does not properly convert characters into bytes.
As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the
getBytes(String enc) method, which takes a
character-encoding name, or the getBytes() method, which
uses the platform's default encoding.- Copies characters from this string into the destination byte
array. Each byte receives the 8 low-order bits of the
corresponding character. The eight high-order bits of each character
are not copied and do not participate in the transfer in any way.
The first character to be copied is at index srcBegin;
the last character to be copied is at index srcEnd-1.
The total number of characters to be copied is
srcEnd-srcBegin. The characters, converted to bytes,
are copied into the subarray of dst starting at index
dstBegin and ending at index:
dstbegin + (srcEnd-srcBegin) - 1
- Parameters:
srcBegin - index of the first character in the string
to copy.srcEnd - index after the last character in the string
to copy.dst - the destination array.dstBegin - the start offset in the destination array.- Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if any of the following
is true:
srcBegin is negative
srcBegin is greater than srcEnd
srcEnd is greater than the length of this
String
dstBegin is negative
dstBegin+(srcEnd-srcBegin) is larger than
dst.length- NullPointerException - if
dst is null
getBytes
public byte[] getBytes(String enc)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
- Convert this
String into bytes according to the specified
character encoding, storing the result into a new byte array.
- Parameters:
enc - A character-encoding name- Returns:
- The resultant byte array
- Throws:
- UnsupportedEncodingException - If the named encoding is not supported
- Since:
- JDK1.1
getBytes
public byte[] getBytes()
- Convert this
String into bytes according to the platform's
default character encoding, storing the result into a new byte array.
- Returns:
- the resultant byte array.
- Since:
- JDK1.1
equals
public boolean equals(Object anObject)
- Compares this string to the specified object.
The result is
true if and only if the argument is not
null and is a String object that represents
the same sequence of characters as this object.
- Parameters:
anObject - the object to compare this String
against.- Returns:
true if the String are equal;
false otherwise.- Overrides:
- equals in class Object
- See Also:
compareTo(java.lang.String),
equalsIgnoreCase(java.lang.String)
equalsIgnoreCase
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
- Compares this
String to another String,
ignoring case considerations. Two strings are considered equal
ignoring case if they are of the same length, and corresponding
characters in the two strings are equal ignoring case.
Two characters c1 and c2 are considered
the same, ignoring case if at least one of the following is true:
- The two characters are the same (as compared by the
== operator).
- Applying the method
java.lang.Character#toUppercase(char)
to each character produces the same result.
- Applying the method java.lang.Character#toLowercase(char)
to each character produces the same result.
- Parameters:
anotherString - the String to compare this
String against.- Returns:
true if the argument is not null
and the Strings are equal,
ignoring case; false otherwise.- See Also:
equals(Object),
Character.toLowerCase(char),
Character.toUpperCase(char)
compareTo
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
- Compares two strings lexicographically.
The comparison is based on the Unicode value of each character in
the strings. The character sequence represented by this
String object is compared lexicographically to the
character sequence represented by the argument string. The result is
a negative integer if this String object
lexicographically precedes the argument string. The result is a
positive integer if this String object lexicographically
follows the argument string. The result is zero if the strings
are equal; compareTo returns 0 exactly when
the equals(Object) method would return true.
This is the definition of lexicographic ordering. If two strings are
different, then either they have different characters at some index
that is a valid index for both strings, or their lengths are different,
or both. If they have different characters at one or more index
positions, let k be the smallest such index; then the string
whose character at position k has the smaller value, as
determined by using the < operator, lexicographically precedes the
other string. In this case, compareTo returns the
difference of the two character values at position k in
the two string -- that is, the value:
this.charAt(k)-anotherString.charAt(k)
If there is no index position at which they differ, then the shorter
string lexicographically precedes the longer string. In this case,
compareTo returns the difference of the lengths of the
strings -- that is, the value:
this.length()-anotherString.length()
- Parameters:
anotherString - the String to be compared.- Returns:
- the value
0 if the argument string is equal to
this string; a value less than 0 if this string
is lexicographically less than the string argument; and a
value greater than 0 if this string is
lexicographically greater than the string argument. - Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
anotherString
is null.
compareTo
public int compareTo(Object o)
- Compares this String to another Object. If the Object is a String,
this function behaves like
compareTo(String). Otherwise,
it throws a ClassCastException (as Strings are comparable
only to other Strings).
- Specified by:
- compareTo in interface Comparable
- Parameters:
o - the Object to be compared.- Returns:
- the value
0 if the argument is a string
lexicographically equal to this string; a value less than
0 if the argument is a string lexicographically
greater than this string; and a value greater than
0 if the argument is a string lexicographically
less than this string. - Throws:
ClassCastException - if the argument is not a
String.- Since:
- JDK1.2
- See Also:
Comparable
compareToIgnoreCase
public int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
- Compares two strings lexicographically, ignoring case considerations.
This method returns an integer whose sign is that of
this.toUpperCase().toLowerCase().compareTo(
str.toUpperCase().toLowerCase()).
Note that this method does not take locale into account,
and will result in an unsatisfactory ordering for certain locales.
The java.text package provides collators to allow
locale-sensitive ordering.
- Parameters:
str - the String to be compared.- Returns:
- a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the
the specified String is greater than, equal to, or less
than this String, ignoring case considerations.
- Since:
- JDK1.2
- See Also:
Collator.compare(String, String)
regionMatches
public boolean regionMatches(int toffset,
String other,
int ooffset,
int len)
- Tests if two string regions are equal.
A substring of this String object is compared to a substring
of the argument other. The result is true if these substrings
represent identical character sequences. The substring of this
String object to be compared begins at index toffset
and has length len. The substring of other to be compared
begins at index ooffset and has length len. The
result is false if and only if at least one of the following
is true:
- toffset is negative.
- ooffset is negative.
- toffset+len is greater than the length of this
String object.
- ooffset+len is greater than the length of the other
argument.
- There is some nonnegative integer k less than len
such that:
this.charAt(toffset+k) != other.charAt(ooffset+k)
- Parameters:
toffset - the starting offset of the subregion in this string.other - the string argument.ooffset - the starting offset of the subregion in the string
argument.len - the number of characters to compare.- Returns:
true if the specified subregion of this string
exactly matches the specified subregion of the string argument;
false otherwise.- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if other is
null.
regionMatches
public boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase,
int toffset,
String other,
int ooffset,
int len)
- Tests if two string regions are equal.
A substring of this String object is compared to a substring
of the argument other. The result is true if these
substrings represent character sequences that are the same, ignoring
case if and only if ignoreCase is true. The substring of
this String object to be compared begins at index
toffset and has length len. The substring of
other to be compared begins at index ooffset and
has length len. The result is false if and only if
at least one of the following is true:
- toffset is negative.
- ooffset is negative.
- toffset+len is greater than the length of this
String object.
- ooffset+len is greater than the length of the other
argument.
- There is some nonnegative integer k less than len
such that:
this.charAt(toffset+k) != other.charAt(ooffset+k)
- ignoreCase is true and there is some nonnegative
integer k less than len such that:
Character.toLowerCase(this.charAt(toffset+k)) !=
Character.toLowerCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k))
and:
Character.toUpperCase(this.charAt(toffset+k)) !=
Character.toUpperCase(other.charAt(ooffset+k))
- Parameters:
ignoreCase - if true, ignore case when comparing
characters.toffset - the starting offset of the subregion in this
string.other - the string argument.ooffset - the starting offset of the subregion in the string
argument.len - the number of characters to compare.- Returns:
true if the specified subregion of this string
matches the specified subregion of the string argument;
false otherwise. Whether the matching is exact
or case insensitive depends on the ignoreCase
argument.
startsWith
public boolean startsWith(String prefix,
int toffset)
- Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix beginning
a specified index.
- Parameters:
prefix - the prefix.toffset - where to begin looking in the string.- Returns:
true if the character sequence represented by the
argument is a prefix of the substring of this object starting
at index toffset; false otherwise.
The result is false if toffset is
negative or greater than the length of this
String object; otherwise the result is the same
as the result of the expression
this.subString(toffset).startsWith(prefix)
- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
prefix is
null.
startsWith
public boolean startsWith(String prefix)
- Tests if this string starts with the specified prefix.
- Parameters:
prefix - the prefix.- Returns:
true if the character sequence represented by the
argument is a prefix of the character sequence represented by
this string; false otherwise.
Note also that true will be returned if the
argument is an empty string or is equal to this
String object as determined by the
equals(Object) method.- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
prefix is
null. - Since:
- JDK1. 0
endsWith
public boolean endsWith(String suffix)
- Tests if this string ends with the specified suffix.
- Parameters:
suffix - the suffix.- Returns:
true if the character sequence represented by the
argument is a suffix of the character sequence represented by
this object; false otherwise. Note that the
result will be true if the argument is the
empty string or is equal to this String object
as determined by the equals(Object) method.- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
suffix is
null.
hashCode
public int hashCode()
- Returns a hashcode for this string. The hashcode for a
String object is computed as
s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1]
using int arithmetic, where s[i] is the
ith character of the string, n is the length of
the string, and ^ indicates exponentiation.
(The hash value of the empty string is zero.)
- Returns:
- a hash code value for this object.
- Overrides:
- hashCode in class Object
indexOf
public int indexOf(int ch)
- Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified character. If a character with value
ch occurs
in the character sequence represented by this String
object, then the index of the first such occurrence is returned --
that is, the smallest value k such that:
this.charAt(k) == ch
is true. If no such character occurs in this string,
then -1 is returned.
- Parameters:
ch - a character.- Returns:
- the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object, or
-1 if the character does not occur.
indexOf
public int indexOf(int ch,
int fromIndex)
- Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified character, starting the search at the specified index.
If a character with value ch occurs in the character
sequence represented by this String object at an index
no smaller than fromIndex, then the index of the first
such occurrence is returned--that is, the smallest value k
such that:
(this.charAt(k) == ch) && (k >= fromIndex)
is true. If no such character occurs in this string at or after
position fromIndex, then -1 is returned.
There is no restriction on the value of fromIndex. If it
is negative, it has the same effect as if it were zero: this entire
string may be searched. If it is greater than the length of this
string, it has the same effect as if it were equal to the length of
this string: -1 is returned.
- Parameters:
ch - a character.fromIndex - the index to start the search from.- Returns:
- the index of the first occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object that is greater
than or equal to
fromIndex, or -1
if the character does not occur.
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(int ch)
- Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
specified character. That is, the index returned is the largest
value k such that:
this.charAt(k) == ch
is true.
The String is searched backwards starting at the last character.
- Parameters:
ch - a character.- Returns:
- the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object, or
-1 if the character does not occur.
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(int ch,
int fromIndex)
- Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of the
specified character, searching backward starting at the specified
index. That is, the index returned is the largest value k
such that:
this.charAt(k) == ch) && (k <= fromIndex)
is true.
- Parameters:
ch - a character.fromIndex - the index to start the search from. There is no
restriction on the value of fromIndex. If it is
greater than or equal to the length of this string, it has
the same effect as if it were equal to one less than the
length of this string: this entire string may be searched.
If it is negative, it has the same effect as if it were -1:
-1 is returned.- Returns:
- the index of the last occurrence of the character in the
character sequence represented by this object that is less
than or equal to
fromIndex, or -1
if the character does not occur before that point.
indexOf
public int indexOf(String str)
- Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified substring. The integer returned is the smallest value
k such that:
this.startsWith(str, k)
is true.
- Parameters:
str - any string.- Returns:
- if the string argument occurs as a substring within this
object, then the index of the first character of the first
such substring is returned; if it does not occur as a
substring,
-1 is returned. - Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
str is
null.
indexOf
public int indexOf(String str,
int fromIndex)
- Returns the index within this string of the first occurrence of the
specified substring, starting at the specified index. The integer
returned is the smallest value k such that:
this.startsWith(str, k) && (k >= fromIndex)
is true.
There is no restriction on the value of fromIndex. If
it is negative, it has the same effect as if it were zero: this entire
string may be searched. If it is greater than the length of this
string, it has the same effect as if it were equal to the length of
this string: -1 is returned.
- Parameters:
str - the substring to search for.fromIndex - the index to start the search from.- Returns:
- If the string argument occurs as a substring within this
object at a starting index no smaller than
fromIndex, then the index of the first character
of the first such substring is returned. If it does not occur
as a substring starting at fromIndex or beyond,
-1 is returned. - Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
str is
null
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(String str)
- Returns the index within this string of the rightmost occurrence
of the specified substring. The rightmost empty string "" is
considered to occur at the index value
this.length().
The returned index is the largest value k such that
this.startsWith(str, k)
is true.
- Parameters:
str - the substring to search for.- Returns:
- if the string argument occurs one or more times as a substring
within this object, then the index of the first character of
the last such substring is returned. If it does not occur as
a substring,
-1 is returned. - Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
str is
null.
lastIndexOf
public int lastIndexOf(String str,
int fromIndex)
- Returns the index within this string of the last occurrence of
the specified substring.
The returned index indicates the start of the substring, and it
must be equal to or less than
fromIndex. That is,
the index returned is the largest value k such that:
this.startsWith(str, k) && (k <= fromIndex)
- Parameters:
str - the substring to search for.fromIndex - the index to start the search from. There is no
restriction on the value of fromIndex. If it is greater than
the length of this string, it has the same effect as if it
were equal to the length of this string: this entire string
may be searched. If it is negative, it has the same effect
as if it were -1: -1 is returned.- Returns:
- If the string argument occurs one or more times as a substring
within this object at a starting index no greater than
fromIndex, then the index of the first character of
the last such substring is returned. If it does not occur as a
substring starting at fromIndex or earlier,
-1 is returned. - Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
str is
null.
substring
public String substring(int beginIndex)
- Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The
substring begins with the character at the specified index and
extends to the end of this string.
Examples:
"unhappy".substring(2) returns "happy"
"Harbison".substring(3) returns "bison"
"emptiness".substring(9) returns "" (an empty string)
- Parameters:
beginIndex - the beginning index, inclusive.- Returns:
- the specified substring.
- Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if
beginIndex is negative or larger than the
length of this String object.
substring
public String substring(int beginIndex,
int endIndex)
- Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The
substring begins at the specified
beginIndex and
extends to the character at index endIndex - 1.
Thus the length of the substring is endIndex-beginIndex.
Examples:
"hamburger".substring(4, 8) returns "urge"
"smiles".substring(1, 5) returns "mile"
- Parameters:
beginIndex - the beginning index, inclusive.endIndex - the ending index, exclusive.- Returns:
- the specified substring.
- Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if the
beginIndex is negative, or
endIndex is larger than the length of
this String object, or
beginIndex is larger than
endIndex.
concat
public String concat(String str)
- Concatenates the specified string to the end of this string.
If the length of the argument string is 0, then this
String object is returned. Otherwise, a new
String object is created, representing a character
sequence that is the concatenation of the character sequence
represented by this String object and the character
sequence represented by the argument string.
Examples:
"cares".concat("s") returns "caress"
"to".concat("get").concat("her") returns "together"
- Parameters:
str - the String that is concatenated to the end
of this String.- Returns:
- a string that represents the concatenation of this object's
characters followed by the string argument's characters.
- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
str is
null.
replace
public String replace(char oldChar,
char newChar)
- Returns a new string resulting from replacing all occurrences of
oldChar in this string with newChar.
If the character oldChar does not occur in the
character sequence represented by this String object,
then a reference to this String object is returned.
Otherwise, a new String object is created that
represents a character sequence identical to the character sequence
represented by this String object, except that every
occurrence of oldChar is replaced by an occurrence
of newChar.
Examples:
"mesquite in your cellar".replace('e', 'o')
returns "mosquito in your collar"
"the war of baronets".replace('r', 'y')
returns "the way of bayonets"
"sparring with a purple porpoise".replace('p', 't')
returns "starring with a turtle tortoise"
"JonL".replace('q', 'x') returns "JonL" (no change)
- Parameters:
oldChar - the old character.newChar - the new character.- Returns:
- a string derived from this string by replacing every
occurrence of
oldChar with newChar.
toLowerCase
public String toLowerCase(Locale locale)
- Converts all of the characters in this
String to lower
case using the rules of the given Locale.
Usually, the characters are converted by calling
Character.toLowerCase.
Exceptions to this rule are listed in
the following table:
| Language Code of Locale |
Upper Case |
Lower Case |
Description |
| tr (Turkish) |
\u0130 |
\u0069 |
capital letter I with dot above -> small letter i |
| tr (Turkish) |
\u0049 |
\u0131 |
capital letter I -> small letter dotless i |
- Parameters:
locale - use the case transformation rules for this locale- Returns:
- the String, converted to lowercase.
- Since:
- JDK1.1
- See Also:
Character.toLowerCase(char),
toUpperCase()
toLowerCase
public String toLowerCase()
- Converts all of the characters in this
String to lower
case using the rules of the default locale, which is returned
by Locale.getDefault.
If no character in the string has a different lowercase version,
based on calling the toLowerCase method defined by
Character, then the original string is returned.
Otherwise, this method creates a new String object that
represents a character sequence identical in length to the character
sequence represented by this String object, with every character
equal to the result of applying the method
Character.toLowerCase to the corresponding character of
this String object.
Examples:
"French Fries".toLowerCase() returns "french fries"
"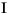
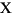
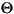
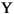
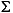 ".toLowerCase() returns "
".toLowerCase() returns "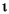
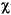

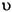
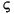 "
"
- Returns:
- the string, converted to lowercase.
- See Also:
Character.toLowerCase(char),
toUpperCase()
toUpperCase
public String toUpperCase(Locale locale)
- Converts all of the characters in this
String to upper
case using the rules of the given locale.
Usually, the characters are converted by calling
Character.toUpperCase.
Exceptions to this rule are listed in
the following table:
| Language Code of Locale |
Lower Case |
Upper Case |
Description |
| tr (Turkish) |
\u0069 |
\u0130 |
small letter i -> capital letter I with dot above |
| tr (Turkish) |
\u0131 |
\u0049 |
small letter dotless i -> capital letter I |
| (all) |
\u00df |
\u0053 \u0053 |
small letter sharp s -> two letters: SS |
- Parameters:
locale - use the case transformation rules for this locale- Returns:
- the String, converted to uppercase.
- Since:
- JDK1.1
- See Also:
Character.toUpperCase(char),
java.lang.String#toLowerCase(char)
toUpperCase
public String toUpperCase()
- Converts all of the characters in this
String to upper
case using the rules of the default locale, which is returned
by Locale.getDefault.
If no character in this string has a different uppercase version,
based on calling the toUpperCase method defined by
Character, then the original string is returned.
Otherwise, this method creates a new String object
representing a character sequence identical in length to the
character sequence represented by this String object and
with every character equal to the result of applying the method
Character.toUpperCase to the corresponding character of
this String object.
Examples:
"Fahrvergnügen".toUpperCase() returns "FAHRVERGNÜGEN"
"Visit Ljubinje!".toUpperCase() returns "VISIT LJUBINJE!"
- Returns:
- the string, converted to uppercase.
- See Also:
Character.toUpperCase(char),
toLowerCase()
trim
public String trim()
- Removes white space from both ends of this string.
If this String object represents an empty character
sequence, or the first and last characters of character sequence
represented by this String object both have codes
greater than '\u0020' (the space character), then a
reference to this String object is returned.
Otherwise, if there is no character with a code greater than
'\u0020' in the string, then a new
String object representing an empty string is created
and returned.
Otherwise, let k be the index of the first character in the
string whose code is greater than '\u0020', and let
m be the index of the last character in the string whose code
is greater than '\u0020'. A new String
object is created, representing the substring of this string that
begins with the character at index k and ends with the
character at index m-that is, the result of
this.substring(k, m+1).
This method may be used to trim
whitespace from the beginning and end
of a string; in fact, it trims all ASCII control characters as well.
- Returns:
- this string, with white space removed from the front and end.
toString
public String toString()
- This object (which is already a string!) is itself returned.
- Returns:
- the string itself.
- Overrides:
- toString in class Object
toCharArray
public char[] toCharArray()
- Converts this string to a new character array.
- Returns:
- a newly allocated character array whose length is the length
of this string and whose contents are initialized to contain
the character sequence represented by this string.
valueOf
public static String valueOf(Object obj)
- Returns the string representation of the
Object argument.
- Parameters:
obj - an Object.- Returns:
- if the argument is
null, then a string equal to
"null"; otherwise, the value of
obj.toString() is returned. - See Also:
Object.toString()
valueOf
public static String valueOf(char[] data)
- Returns the string representation of the
char array
argument. The contents of the character array are copied; subsequent
modification of the character array does not affect the newly
created string.
- Parameters:
data - a char array.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string representing the same sequence of
characters contained in the character array argument.
valueOf
public static String valueOf(char[] data,
int offset,
int count)
- Returns the string representation of a specific subarray of the
char array argument.
The offset argument is the index of the first
character of the subarray. The count argument
specifies the length of the subarray. The contents of the subarray
are copied; subsequent modification of the character array does not
affect the newly created string.
- Parameters:
data - the character array.offset - the initial offset into the value of the
String.count - the length of the value of the String.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string representing the sequence of
characters contained in the subarray of the character array
argument.
- Throws:
- NullPointerException - if
data is
null.- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if
offset is
negative, or count is negative, or
offset+count is larger than
data.length.
copyValueOf
public static String copyValueOf(char[] data,
int offset,
int count)
- Returns a String that is equivalent to the specified character array.
It creates a new array and copies the characters into it.
- Parameters:
data - the character array.offset - initial offset of the subarray.count - length of the subarray.- Returns:
- a
String that contains the characters of the
specified subarray of the character array.
copyValueOf
public static String copyValueOf(char[] data)
- Returns a String that is equivalent to the specified character array.
It creates a new array and copies the characters into it.
- Parameters:
data - the character array.- Returns:
- a
String that contains the characters of the
character array.
valueOf
public static String valueOf(boolean b)
- Returns the string representation of the
boolean argument.
- Parameters:
b - a boolean.- Returns:
- if the argument is
true, a string equal to
"true" is returned; otherwise, a string equal to
"false" is returned.
valueOf
public static String valueOf(char c)
- Returns the string representation of the
char
argument.
- Parameters:
c - a char.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string of length
1 containing
as its single character the argument c.
valueOf
public static String valueOf(int i)
- Returns the string representation of the
int argument.
The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Integer.toString method of one argument.
- Parameters:
i - an int.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string containing a string representation of
the
int argument. - See Also:
Integer.toString(int, int)
valueOf
public static String valueOf(long l)
- Returns the string representation of the
long argument.
The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Long.toString method of one argument.
- Parameters:
l - a long.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string containing a string representation of
the
long argument. - See Also:
Long.toString(long)
valueOf
public static String valueOf(float f)
- Returns the string representation of the
float argument.
The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Float.toString method of one argument.
- Parameters:
f - a float.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string containing a string representation of
the
float argument. - See Also:
Float.toString(float)
valueOf
public static String valueOf(double d)
- Returns the string representation of the
double argument.
The representation is exactly the one returned by the
Double.toString method of one argument.
- Parameters:
d - a double.- Returns:
- a newly allocated string containing a string representation of
the
double argument. - See Also:
Double.toString(double)
intern
public String intern()
- Returns a canonical representation for the string object.
A pool of strings, initially empty, is maintained privately by the
class String.
When the intern method is invoked, if the pool already contains a
string equal to this String object as determined by
the equals(Object) method, then the string from the pool is
returned. Otherwise, this String object is added to the
pool and a reference to this String object is returned.
It follows that for any two strings s and t,
s.intern() == t.intern() is true
if and only if s.equals(t) is true.
All literal strings and string-valued constant expressions are
interned. String literals are defined in §3.10.5 of the
Java Language
Specification
- Returns:
- a string that has the same contents as this string, but is
guaranteed to be from a pool of unique strings.
Submit a bug or feature Version 1.2 of Java Platform API Specification
Java is a trademark or registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the US and other countries.
Copyright 1993-1998 Sun Microsystems, Inc. 901 San Antonio Road,
Palo Alto, California, 94303, U.S.A. All Rights Reserved.
".toLowerCase() returns "
"