






In this material you have learned about:
- Objects which are used to hold data and behaviour about specific entities in our system or model.
- Classes which are used to represent categories of objects with identical data and behaviour.
In object-orientation we may form hierarchies of categories (classes), by letting classes inherit the operations, methods and attributes from a "base class" or "super class".
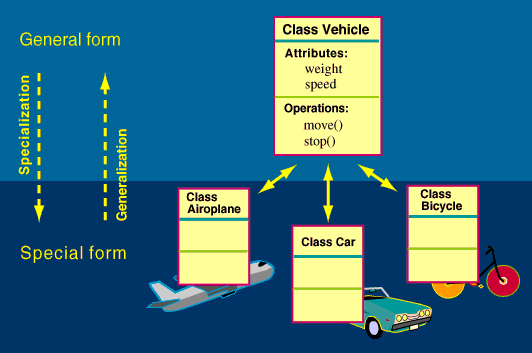
Inheritance defines the "is-a" or "is-a-kind-of" hierarchy between classes.
Aircraft, Cars and Bicycles are all Vehicles, and share some common properties of a Vehicle, namely the attributes speed and weight and the operations move and stop. The class Vehicle is a generalization of the classes Aircraft, Car and Bicycle. Aircraft, Car and Bicycle are specializations of the class Vehicle.
In the terminology of object-oriented programming: Vehicle is the Base class or Superclass, while car is a Subclass or Derived class.
How to Use Inheritance
Inheritance may be used for:
- Sharing operations and attributes between classes to avoid unneccesary duplication of code.
- Modelling specialization and generalization in the real world.
- Writing general software components as "superclasses", which may be extended and tailored to specific needs in "subclasses".
 Here is an example of inheritance in the C++ language.
Here is an example of inheritance in the C++ language.
 Here is an example of inheritance in Modelling Diagrams.
Here is an example of inheritance in Modelling Diagrams.
previous |
next |
start |
contents |
dictionary |
help |
evaluation
© Ericsson Telecom AB, 1995, Stockholm, Sweden

















 Here is an example of inheritance in the C++ language.
Here is an example of inheritance in the C++ language. Here is an example of inheritance in Modelling Diagrams.
Here is an example of inheritance in Modelling Diagrams.